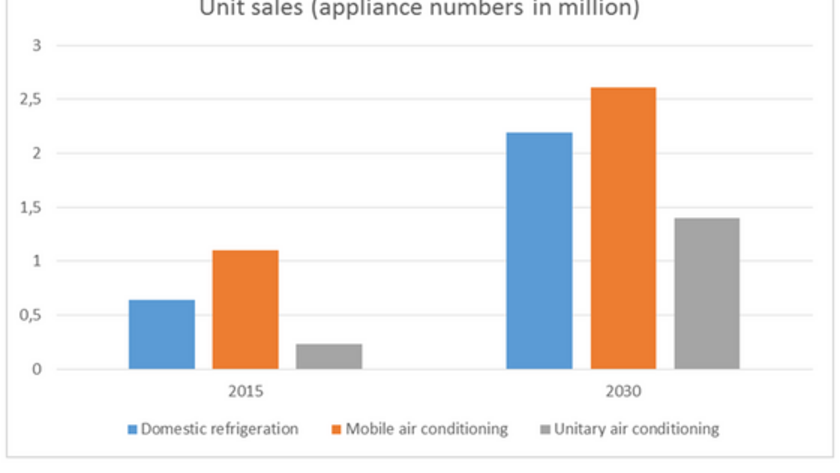
With a population of 53 million, an urbanisation rate of 63.3% and an electrification rate of 79.8%, South Africa's stock of cooling appliances is quite large compared to most other African countries: In 2014, the country had in use an estimated 1.33 billion domestic refrigerators, 840 million car air conditioners and 757 million unitary air conditioning appliances (All numbers according to GCI calculations - for more information see the GCI country data (opens in a new window)). Expected unit sales in these sectors are estimated to triple by 2030 (Figure 1).
The estimated overall emissions from the RAC sectors amount to 32.2 Mt CO2eq in 2015 (Figure 2).
In a business-as-usual scenario, this number is expected to rise to 81.1 Mt CO2eq in the year 2030. However, an estimated 29.4 Mt CO2eq could be saved in 2030 when considering the use of climate friendly natural refrigerants, changes in the system design and improvements in the energy efficiency (Figure 3).
About 40 % of the total emission reduction potential can be achieved through a change to climate friendly natural refrigerants (Figure 4).
You can also find this data – and much more – by conducting your own research on the GCI website at www.green-cooling-initiative.org/country-data (opens in a new window).
*In this rubric, we want to give some insight into the potential of emissions savings in the refrigeration and air conditioning sectors by showing data and figures related to one specific country. We will pick a different country each time. If you would like to have your country portrayed in one of the next newsletters, please send us your suggestion.